
The hurricane that brought Newfoundland the 'worst flooding in 100 years'
On this day in weather history, Hurricane Gabrielle impacted Newfoundland.
This Day In Weather History is a daily podcast by Chris Mei from The Weather Network, featuring stories about people, communities and events and how weather impacted them.
--
On Wednesday, Sept. 19, 2001, Hurricane Gabrielle impacted Newfoundland, bringing the "worst flooding in 100 years."
Gabrielle caused extensive flooding in Florida and Newfoundland. On Sept. 11, it developed in the Gulf of Mexico. The storm formed on the same day as the Sept. 11 attacks, so flights were cancelled across the United States. On Sept. 14, Gabrielle hit Florida, shuttering flights for a third day in a row for the state.
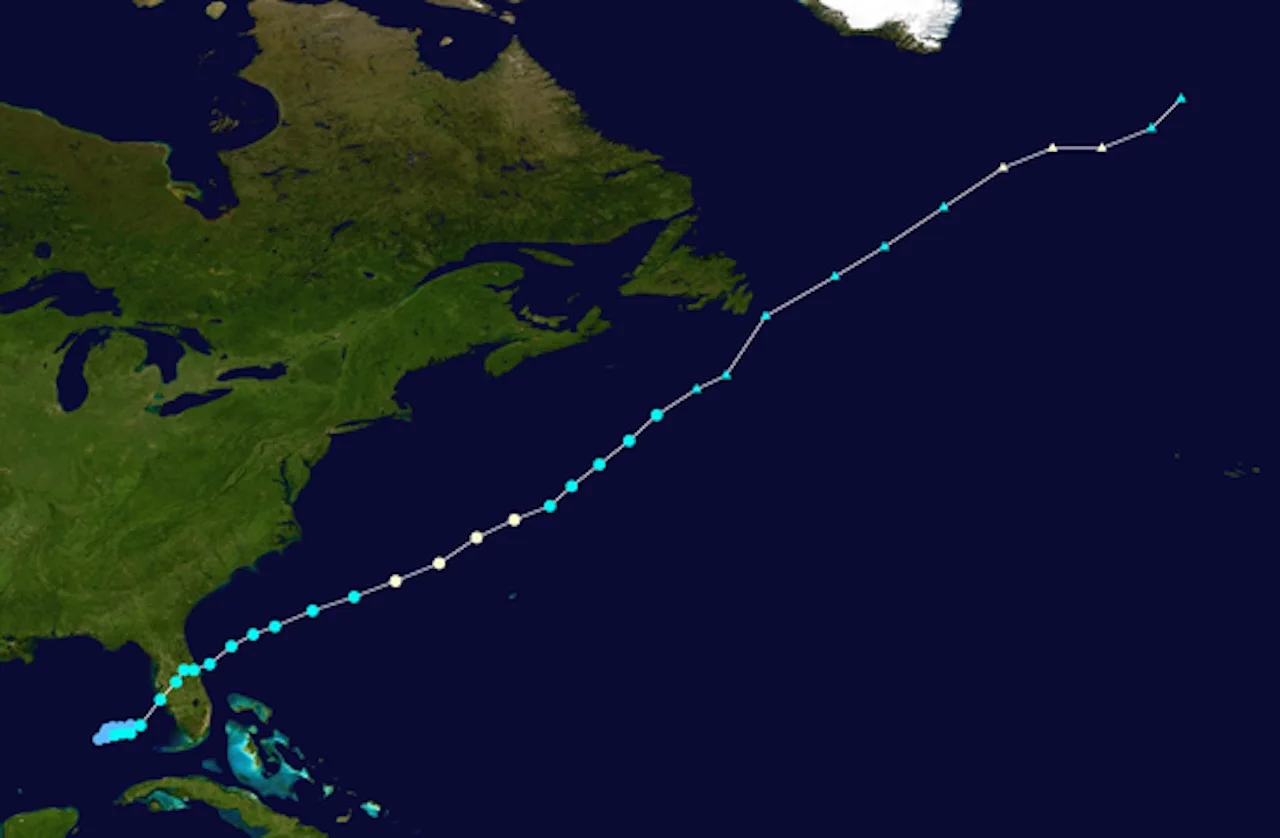
"Map plotting the track and the intensity of the storm, according to the Saffir–Simpson scale." Courtesy of Wikipedia
The hurricane made landfall just south of the Tampa Bay area, with winds as strong as 110 km/h. Gabrielle also brought heavy rainfall, up to 380 mm. The storm left 696,000 customers without power across the state. The hurricane also caused three deaths, due to high waves and flooding. In total, the storm caused around US$230 million (2001) in damages in Florida.
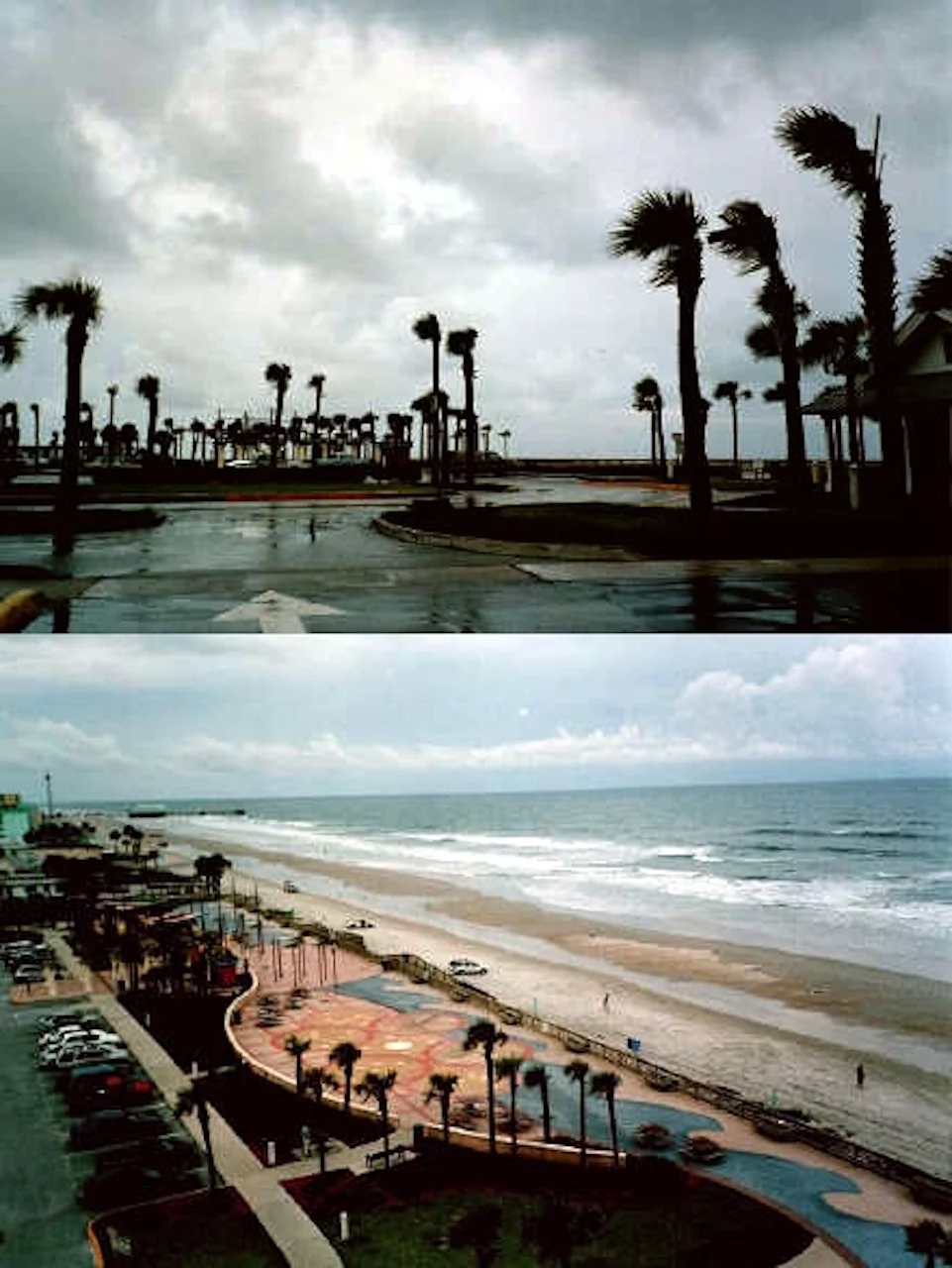

"Daytona Beach during Gabrielle." Courtesy of Wikipedia
After leaving Florida, Gabrielle weakened but re-intensified into a hurricane on Sept. 17. On Sep. 19, the hurricane weakened into an extratropical cyclone as it passed just southeast of Newfoundland. The storm brought record rainfall to the province.
St. John's mayor said that Gabrielle was "the worst storm in 100 years." The heavy rainfall flooded homes, schools, and businesses. Floods overtook two roads and severely impacted 20 others. The storm left thousands without power or phone service.
To learn more about Hurricane Gabrielle, listen to today's episode of "This Day In Weather History."
Subscribe to 'This Day in Weather History': Apple Podcasts | Amazon Alexa | Google Assistant | Spotify | Google Podcasts | iHeartRadio | Overcast'
Thumbnail: Courtesy of NOAA










